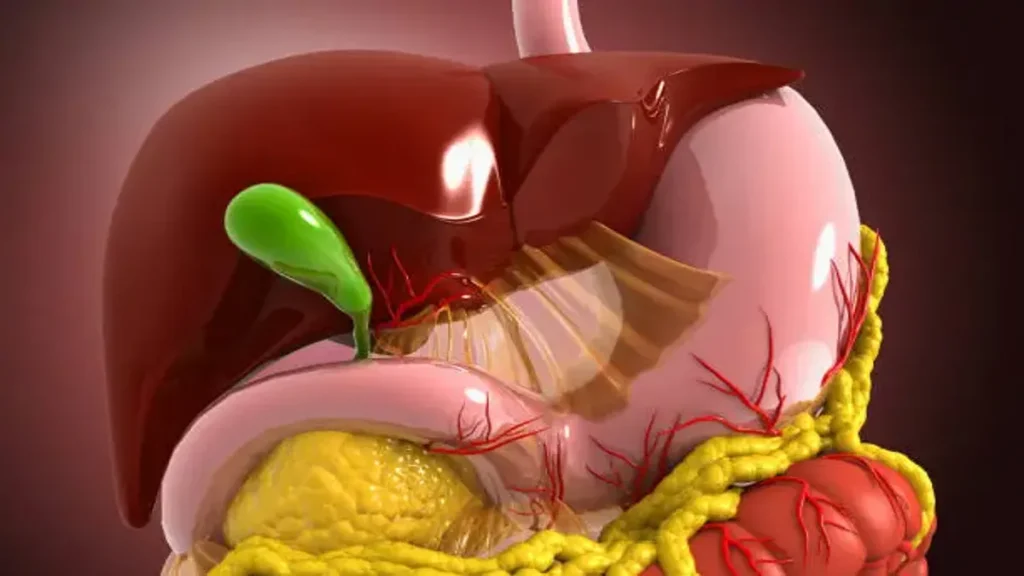
Cholecistitas, more commonly recognized in English as cholecystitis, refers to inflammation of the gallbladder, the small pear-shaped organ located under the liver that stores and releases bile. For anyone searching about this condition today, the key question is immediate: What exactly is cholecistitas and why is it significant? The answer is straightforward yet vital. Cholecistitas is an inflammatory condition often triggered by gallstones blocking bile ducts, leading to pain, infection, and potentially serious complications if untreated. It is one of the most common gastrointestinal emergencies, and while manageable, it requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Within the first hundred words, the searcher’s intent is answered clearly: cholecistitas is gallbladder inflammation, a condition requiring careful medical attention and, in many cases, surgical or medical intervention.
Anatomy of the Gallbladder
To understand cholecistitas, it is important first to examine the gallbladder’s role in the body. The gallbladder sits just beneath the liver, holding bile, a digestive fluid rich in salts and enzymes that help break down fats. When we eat fatty foods, the gallbladder contracts, releasing bile into the small intestine. While the organ is not essential for survival, it plays a supportive role in digestion. Inflammation disrupts this process, creating pain, digestive imbalance, and risk of infection.
“The gallbladder is an unsung organ. We don’t notice it until something goes wrong—and then it demands attention.”
What Causes Cholecistitas?
The primary cause of cholecistitas is gallstones. These hardened deposits of cholesterol or bile salts block the cystic duct, preventing bile flow. Blockage triggers swelling, infection, and inflammation. However, gallstones are not the only cause.
Other triggers include:
- Bile Duct Problems: Strictures or tumors blocking flow.
- Infections: Bacterial infections, especially E. coli or Klebsiella.
- Trauma or Surgery: Injury to the abdominal region.
- Critical Illness: Inflammation sometimes arises in patients with severe burns or systemic infections.
- Parasitic Infections: Rare, but reported in tropical regions.
Types of Cholecistitas
There are two main forms of the condition:
- Acute Cholecistitas: A sudden, severe inflammation often caused by gallstones. Requires urgent medical care.
- Chronic Cholecistitas: Long-term irritation and inflammation, usually due to repeated gallstone attacks. Leads to gallbladder scarring and dysfunction.
Both conditions carry risks, but acute cholecistitas is typically more dangerous due to immediate infection risk.
Table 1: Types of Cholecistitas
| Type | Key Characteristics | Risks Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Cholecistitas | Sudden pain, fever, gallstone obstruction | Infection, perforation, emergency surgery |
| Chronic Cholecistitas | Ongoing irritation, scarring of gallbladder | Reduced function, recurring pain, surgery |
Symptoms of Cholecistitas
The condition presents with a recognizable set of symptoms.
- Abdominal Pain: Sharp pain in the upper right or center abdomen, often after eating fatty meals.
- Radiating Pain: Discomfort spreading to the right shoulder or back.
- Fever and Nausea: Signals infection and systemic inflammation.
- Tenderness: Particularly when pressing on the abdomen.
- Digestive Upset: Bloating, indigestion, vomiting.
One patient described the pain as:
“It felt like a fire lit in my side, constant and unrelenting, making every breath hurt.”
Diagnosis
Physicians use several approaches to confirm cholecistitas:
- Physical Exam: Tenderness in the right upper quadrant.
- Blood Tests: Elevated white blood cell counts suggest infection.
- Ultrasound: Primary diagnostic tool for gallstones and gallbladder swelling.
- CT or MRI: Used in complicated cases to assess extent of inflammation.
- HIDA Scan: Specialized imaging that tracks bile movement.
Accurate diagnosis is critical since untreated inflammation may lead to gallbladder rupture.
Complications
If left untreated, cholecistitas can escalate.
- Gangrene: Tissue death in the gallbladder.
- Perforation: Rupture leading to bile leakage and infection.
- Sepsis: Systemic infection spreading through the bloodstream.
- Gallbladder Abscess: Pus-filled cavity requiring drainage.
- Digestive Dysfunction: Long-term chronic pain and poor fat digestion.
Table 2: Potential Complications of Cholecistitas
| Complication | Description | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Gangrene | Death of gallbladder tissue | High, requires emergency surgery |
| Perforation | Gallbladder rupture and bile leakage | Life-threatening, immediate intervention |
| Sepsis | Widespread infection | Critical, intensive care required |
| Abscess | Pus collection within or near gallbladder | Requires drainage and antibiotics |
| Chronic Dysfunction | Ongoing digestive issues | Long-term health impact |
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on severity.
- Hospitalization: Most acute cases require admission.
- Antibiotics: Targeting infection-causing bacteria.
- Fasting: Resting the gallbladder by restricting oral intake.
- IV Fluids and Pain Relief: Supporting recovery.
- Surgery: Cholecystectomy, or gallbladder removal, is the standard treatment.
For chronic cases, elective surgery may be recommended to prevent repeated attacks.
“Removing the gallbladder is not about loss—it’s about restoring health and preventing future crises,” a surgeon explained.
Lifestyle and Prevention
While not all cases are preventable, risk can be reduced through lifestyle changes:
- Maintain Healthy Weight: Obesity increases gallstone risk.
- Balanced Diet: Limit saturated fats, emphasize fiber.
- Exercise: Regular activity reduces bile stasis.
- Avoid Crash Diets: Rapid weight loss can trigger gallstone formation.
- Hydration: Supports bile fluidity.
Bullet-Point Insights for Readers
- Cholecistitas is gallbladder inflammation, often triggered by gallstones.
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and tenderness.
- Untreated cases may lead to dangerous complications such as perforation or sepsis.
- Diagnosis relies on imaging, especially ultrasound.
- Standard treatment often involves antibiotics and gallbladder removal surgery.
- Prevention includes diet, exercise, and weight management.
Cultural and Public Health Perspectives
In many cultures, gallbladder disease has been linked to dietary patterns. Diets high in fried foods and saturated fats increase risk. Public health campaigns now emphasize balanced nutrition not just for heart health, but also to reduce gallstone-related diseases. In countries with advanced healthcare, gallbladder removal is a routine surgery. In low-resource regions, however, untreated cholecistitas remains a major cause of morbidity.
“A plate of food is not just calories—it is a reflection of long-term health risks, including gallstones.”
The Emotional Dimension of Cholecistitas
Beyond medical facts, patients experience fear, uncertainty, and anxiety. For many, the sudden onset of severe abdominal pain is alarming. Some describe relief after surgery as life-changing, while others struggle with adjusting to life without a gallbladder, facing digestive changes.
Advances in Treatment
Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery has transformed outcomes. Instead of large incisions, surgeons now remove the gallbladder through small cuts, reducing recovery times. Research also explores non-surgical solutions, such as medications that dissolve gallstones, though these remain limited in effectiveness.
Global Perspective
Cholecistitas affects populations worldwide, with higher prevalence in women, especially those over 40, and individuals with obesity or high-fat diets. Public health agencies monitor gallbladder disease as part of gastrointestinal illness tracking. The condition reflects broader global issues: lifestyle changes, dietary shifts, and access to surgical care.
Quotes That Resonate
“Pain is the first language of the gallbladder.”
“Treating cholecistitas is not just about removing an organ—it’s about restoring balance in the digestive system.”
“Every case of gallbladder inflammation is a reminder that small organs can cause large problems.”
Conclusion
Cholecistitas, though centered on a small organ, carries significant health consequences. It begins with inflammation, often caused by gallstones, but can progress into life-threatening complications if ignored. For patients, timely diagnosis and treatment—often surgery—restore quality of life. For society, prevention through lifestyle, diet, and awareness can reduce its prevalence. The gallbladder may be small, but its role in health and disease is profound. Cholecistitas remains a condition where medical science, lifestyle choices, and public health intersect.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cholecistitas
1. What is cholecistitas?
Cholecistitas, or cholecystitis, is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstones blocking bile ducts, leading to pain and infection.
2. What are the common symptoms?
The main symptoms include sharp abdominal pain (often in the upper right side), nausea, vomiting, fever, tenderness, and digestive upset.
3. How is cholecistitas diagnosed?
Doctors typically use ultrasound imaging, blood tests for infection markers, and sometimes CT or MRI scans to confirm gallbladder inflammation.
4. What treatments are available?
Treatment may include antibiotics, hospitalization, pain relief, fasting, and in most cases, gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy).
5. Can cholecistitas be prevented?
Prevention focuses on maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats, staying active, and avoiding crash diets.