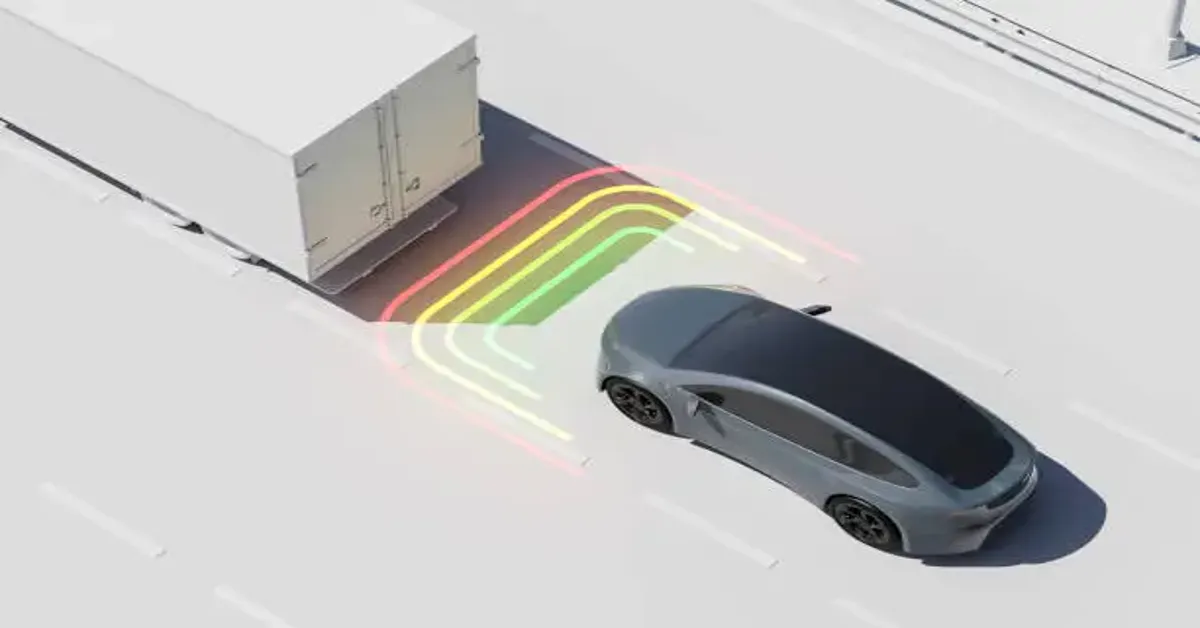
If your dashboard has ever flashed “StabiliTrak Service Needed,” you’re not alone—and understanding what this system does can mean the difference between a safe drive and a slippery mishap. StabiliTrak is General Motors’ proprietary electronic stability control system designed to help drivers maintain control of their vehicles in adverse conditions. It’s more than just a buzzword tucked into your owner’s manual; it’s a key part of modern vehicle safety.
From wet roads to sudden swerves, StabiliTrak is working quietly behind the scenes, adjusting braking and engine power to help you stay on course. But how does it really work, and what happens when it fails? This guide will unpack the mechanics, benefits, warning signs, and limitations of StabiliTrak, giving you a full picture of this essential but often misunderstood safety feature.
What is StabiliTrak?
StabiliTrak is an electronic stability control (ESC) system developed by General Motors. It’s designed to detect and reduce loss of traction, assisting drivers in maintaining vehicle control. It achieves this by monitoring various sensors and intervening when it senses oversteer or understeer—essentially when your car is not going where you’re steering.
In simpler terms, Stabili-Trak acts as an invisible co-pilot. When you’re turning or driving on slippery roads, it makes small corrections that help keep your vehicle stable, preventing spin-outs or skids.
Quick Overview of How It Works
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensors | Measure speed of each wheel to detect slipping or skidding |
| Steering Angle Sensor | Reads the direction the driver wants to go |
| Yaw Rate Sensor | Monitors the car’s rotational movement around its vertical axis |
| Brake and Engine Control Modules | Intervene by reducing engine power or applying brakes to individual wheels |
The Origin and Purpose of Stability Control Systems
Electronic Stability Control (ESC), including GM’s StabiliTrak, was introduced in the early 2000s and became mandatory in the U.S. on all new passenger vehicles after 2012. The system evolved from earlier traction control technologies, which were primarily concerned with limiting wheel spin.
Unlike simple traction control, Stabili-Trak works even when you’re not accelerating, which makes it crucial in avoiding accidents caused by loss of control in corners or during emergency maneuvers. The system is most active during unexpected driving situations—such as avoiding a deer, hydroplaning, or swerving on ice.
When and Why StabiliTrak Engages
StabiliTrak doesn’t operate all the time; it activates only when necessary. Here are common driving situations when the system kicks in:
- Driving on wet or icy roads: When your car begins to fishtail or skid.
- Taking sharp turns at high speed: Corrects understeering or oversteering.
- Sudden evasive maneuvers: Helps regain directional control.
- Uneven road conditions: Compensates for slipping on gravel or dirt shoulders.
In these moments, Stabili-Trak may reduce engine torque, apply brake pressure to individual wheels, or do both to bring the vehicle back in line with the intended direction.
Difference Between StabiliTrak and Traction Control
Many drivers confuse StabiliTrak with traction control, but they serve different functions.
| Feature | StabiliTrak | Traction Control |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Maintains directional control (steering) | Prevents wheel spin during acceleration |
| Operating Conditions | Engages when vehicle oversteers or understeers | Works mostly during low-speed acceleration or from a stop |
| Sensor Inputs | Uses steering angle, yaw, and speed sensors | Uses only wheel speed sensors |
| Intervention Method | Brakes individual wheels and adjusts engine torque | Reduces engine power or applies brake to spinning wheel |
The two systems complement each other. Traction control gets you moving safely, while StabiliTrak helps keep you on the right path once you’re in motion.
Common StabiliTrak Warning Lights and Messages
If something’s wrong with the system, your vehicle will alert you with messages such as:
- “Service StabiliTrak”
- “StabiliTrak Off”
- “Traction Control Off”
These warnings can be triggered by several issues—not necessarily a malfunction within the Stabili-Trak system itself.
Possible Causes
| Issue | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor | Can’t measure individual wheel speed accurately |
| Malfunctioning Steering Angle Sensor | Mismatched input between wheel direction and steering input |
| Brake Switch Problems | Brake pedal position not recognized |
| Battery or Charging System Fault | Low voltage affects electronic systems |
| ABS Module Malfunction | Shared components may disrupt stability control functions |
If the warning comes on and stays on, the StabiliTrak system has likely been disabled, meaning your vehicle no longer has ESC protection.
What to Do When the StabiliTrak Light Comes On
A warning light doesn’t always mean immediate danger, but it should be taken seriously. Here’s what you can do:
- Pull Over Safely: If the vehicle is handling poorly, pull over and restart the engine.
- Restart the Vehicle: Sometimes, the system can reset itself after a restart.
- Check the Battery: A weak or dying battery can cause false readings.
- Visit a Mechanic: If the light remains, diagnostic tools can pinpoint the issue.
It’s safe to drive short distances without Stabili-Trak under normal conditions, but you should avoid slippery or aggressive driving until it’s repaired.
Can You Turn Off StabiliTrak?
Yes—but usually only temporarily. Many GM vehicles allow drivers to disable the system under specific conditions (like driving off-road or in deep snow), though it automatically reactivates at the next restart.
To disable it:
- Locate the “Traction Control” or “StabiliTrak” button (often on the center console or dash).
- Press and hold for several seconds until the dashboard confirms it’s off.
Disabling it should be done with caution. In most everyday driving scenarios, StabiliTrak provides essential safety.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Regular maintenance can help keep the StabiliTrak system running optimally. Here’s a quick checklist:
| Component | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|
| Tire Condition | Ensure even wear; mismatched tires can confuse the system |
| Wheel Speed Sensors | Keep clean and free from debris or corrosion |
| Brake System | Check brake pads, fluid levels, and calipers regularly |
| Electrical System | A strong battery and clean terminals support consistent sensor data |
| Software Updates | Ask your dealer about firmware updates during regular service visits |
Real-World Impact and Safety Benefits
According to crash data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESC systems reduce single-vehicle crashes by up to 50%, especially on wet or icy roads. While the name “StabiliTrak” is brand-specific, its benefits are part of a broader category of accident-prevention technology.
StabiliTrak is especially valuable in:
- Rural and mountainous driving
- Rainy or snowy climates
- High-speed highway travel
- Emergency evasive maneuvers
Drivers who learn to trust the system—but not depend on it blindly—tend to benefit the most.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Despite its advantages, misinformation about StabiliTrak is common. Let’s clear up some myths.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| StabiliTrak can prevent all skids | It reduces risk, but physics still apply—like excessive speed on ice |
| It’s broken if the warning light flashes once | Temporary glitches can happen; only persistent alerts require attention |
| It replaces the need for good tires | Tires are still your first line of defense |
| StabiliTrak works like AWD | ESC systems manage stability; they don’t affect power distribution like AWD |
| You must tow your car if it fails | Not true, unless the vehicle becomes hard to control |
StabiliTrak in Different GM Models
StabiliTrak is standard or optional on nearly all GM vehicles, including:
- Chevrolet Silverado, Equinox, Malibu
- GMC Sierra, Acadia
- Buick Encore, Enclave
- Cadillac Escalade, XT5
In performance or SUV variants, the system may have selectable drive modes (e.g., Snow, Sport, Tow) that adjust StabiliTrak sensitivity.
How the System is Evolving
Newer versions of StabiliTrak are more than just stability systems—they integrate with lane-keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and collision mitigation. As vehicle technology advances, StabiliTrak is becoming a foundational layer for semi-autonomous driving features.
Integration With Other Safety Tech
| Feature | StabiliTrak Interaction |
|---|---|
| Automatic Emergency Braking | ESC can help prevent overcorrection post-braking |
| Lane Keep Assist | ESC aids in maintaining lane trajectory after correction |
| Hill Start Assist | ESC cooperates to prevent rollback on slopes |
| Driver Attention Monitors | If drowsy driving is detected, StabiliTrak preps for emergency events |
Final Thoughts: Is StabiliTrak Worth Understanding?
Absolutely. StabiliTrak is one of those systems you don’t think about—until it saves you from a potential accident. While not a substitute for attentive driving, it provides a significant safety net in unpredictable conditions. Understanding how it works, recognizing warning signs, and knowing what to do when it fails gives you control over your vehicle—and peace of mind on the road.
Modern vehicles are evolving into intelligent machines. StabiliTrak represents a step toward a world where cars can compensate for human error. That’s not just technology—it’s a safety revolution, quietly keeping you safe every mile you drive.
FAQs
1. What is StabiliTrak and how does it work?
StabiliTrak is General Motors’ electronic stability control system designed to help drivers maintain control of their vehicle in slippery or emergency conditions. It works by monitoring wheel speed, steering angle, and vehicle direction. If it detects a loss of traction or the car veering off course, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels and may reduce engine power to help realign the vehicle with the driver’s intended path.
2. What does “Service StabiliTrak” mean on my dashboard?
When your dashboard displays “Service StabiliTrak,” it indicates the system has detected a fault or error, and stability control may be disabled. This can be caused by sensor issues, low battery voltage, faulty brake switches, or problems with the ABS system. While your car may still be drivable, you should have it diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible to ensure full safety functionality.
3. Can I drive my car with the StabiliTrak light on?
Yes, you can drive your car with the StabiliTrak light on under normal road conditions, but it’s not recommended for slippery or high-speed environments. The light means that the system is not actively protecting you from skidding or sliding. It’s best to drive cautiously and schedule a repair to restore full safety capabilities.
4. Is StabiliTrak the same as traction control or all-wheel drive?
No, StabiliTrak is not the same as traction control or all-wheel drive (AWD). While traction control limits wheel spin during acceleration, StabiliTrak manages the vehicle’s overall direction by correcting oversteer or understeer. AWD distributes power to all four wheels but doesn’t actively correct your direction like StabiliTrak does. These systems are complementary, but they serve different purposes.
5. Can I turn off StabiliTrak, and should I?
Yes, most GM vehicles allow you to temporarily turn off StabiliTrak—usually via a button on the dashboard or center console. However, disabling it should only be done in specific scenarios, such as when driving off-road, in deep snow, or when stuck. Under normal driving conditions, it’s safer to keep StabiliTrak enabled, as it plays a critical role in maintaining vehicle stability.